

#Git status remove untracked files how to#
Managing untracked files is essential for maintaining a clean and organized repository, ensuring efficient collaboration, and protecting sensitive information.īy understanding untracked files and learning how to remove them, you can harness the power of Git and elevate your development skills. They can occur due to new files, ignored files, modifications to tracked files, or file deletions. Untracked files are files in your local Git repository that Git is not currently monitoring. By removing these files, you enhance the security of your project.
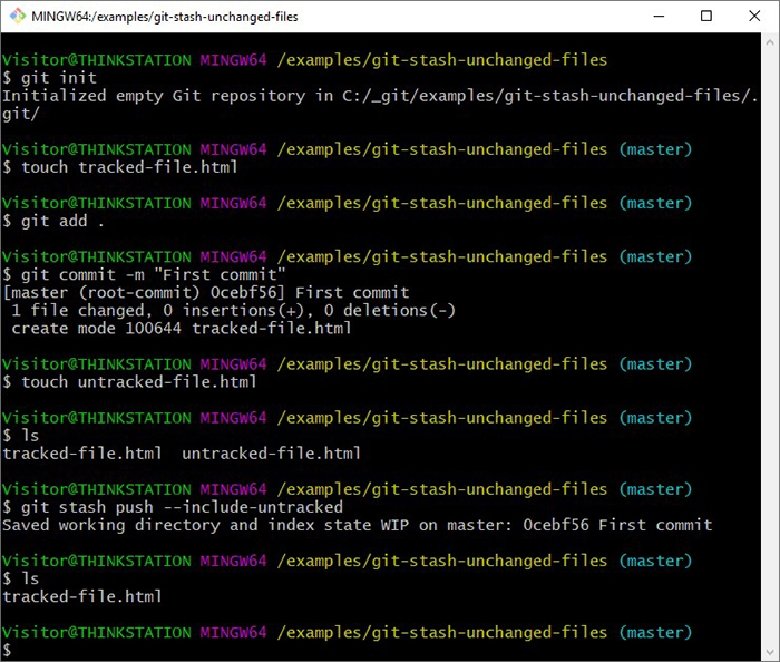
Security and privacy: Untracked files might contain sensitive information or credentials that should not be shared or committed to the repository.By regularly removing untracked files, you minimize the chances of unnecessary conflicts and ensure a smooth version control workflow. Efficient version control: Untracked files can lead to accidental commits or conflicts when collaborating with other team members.This simplifies collaboration and reduces confusion for other developers working on the project. Clutter-free repository: By removing untracked files, you keep your repository clean and focused only on relevant files.It's crucial to manage untracked files effectively for several reasons: Deleted files: If you delete a tracked file directly from your project directory, Git considers it an untracked file since it no longer exists in the repository.Modified tracked files: If you modify a file that is already being tracked by Git, the modified version becomes an untracked file until you stage and commit the changes.Ignored files will not be tracked by Git, and they remain untracked. Ignored files: Git provides a mechanism to ignore certain files or directories using a.These files are considered untracked until you explicitly add them to the repository. New files: When you create a new file in your project directory, Git does not automatically start tracking it.Untracked files can occur in various scenarios, such as: This means that Git is unaware of any modifications made to these files. Untracked files are files that exist in your local repository but are not being tracked by Git. However, it does not automatically track all files in your project directory. When working with a Git repository, Git keeps track of changes made to files. In this section, we will delve deeper into the concept of untracked files and their significance in Git. Untracked files are an essential concept in Git that every developer should understand. For more information, read our affiliate disclosure. If you click an affiliate link and subsequently make a purchase, we will earn a small commission at no additional cost to you (you pay nothing extra). Important disclosure: we're proud affiliates of some tools mentioned in this guide. Embrace the adventure, unravel the mysteries, and unlock the true potential of Git's hidden gems. Harness the ability to remove, ignore, and conquer untracked files, transforming your development journey into a seamless symphony of code. Unveil the secrets of untracked files, learn how to navigate their treacherous paths, and emerge as a Git virtuoso. They hold the power to clutter your repository, sow confusion, and hinder collaboration. In the realm of Git, untracked files lurk in the shadows, awaiting discovery. Unravel the Mystery of Untracked Files: Mastering the Art of Git's Hidden Gems. -e or -exclude – Use the given exclude pattern in addition to the standard ignore rules.Why did the untracked file go on a vacation?īecause it wanted to escape the committed life!.-i or -interactive – Show what would be done and clean files interactively.If any paths are specified, -d is irrelevant all untracked files matching the specified paths (with exceptions for nested git directories mentioned under -force) will be removed. Specify -d to have it recurse into such directories as well. -d – Normally, when no is specified, git clean will not recurse into untracked directories to avoid removing too much.git subdirectory) unless a second -f is given. Git will refuse to modify untracked nested git repositories (directories with a. -f or -force – If the Git configuration variable clean.requireForce is not set to false, git clean will refuse to delete files or directories unless given -f or -i.-n or -dry-run – Show the list of files that would be removed without actually removing.git clean – Remove untracked files from the working tree.Important noteĪlways use -n or -dry-run before running the command.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
